Table of Contents
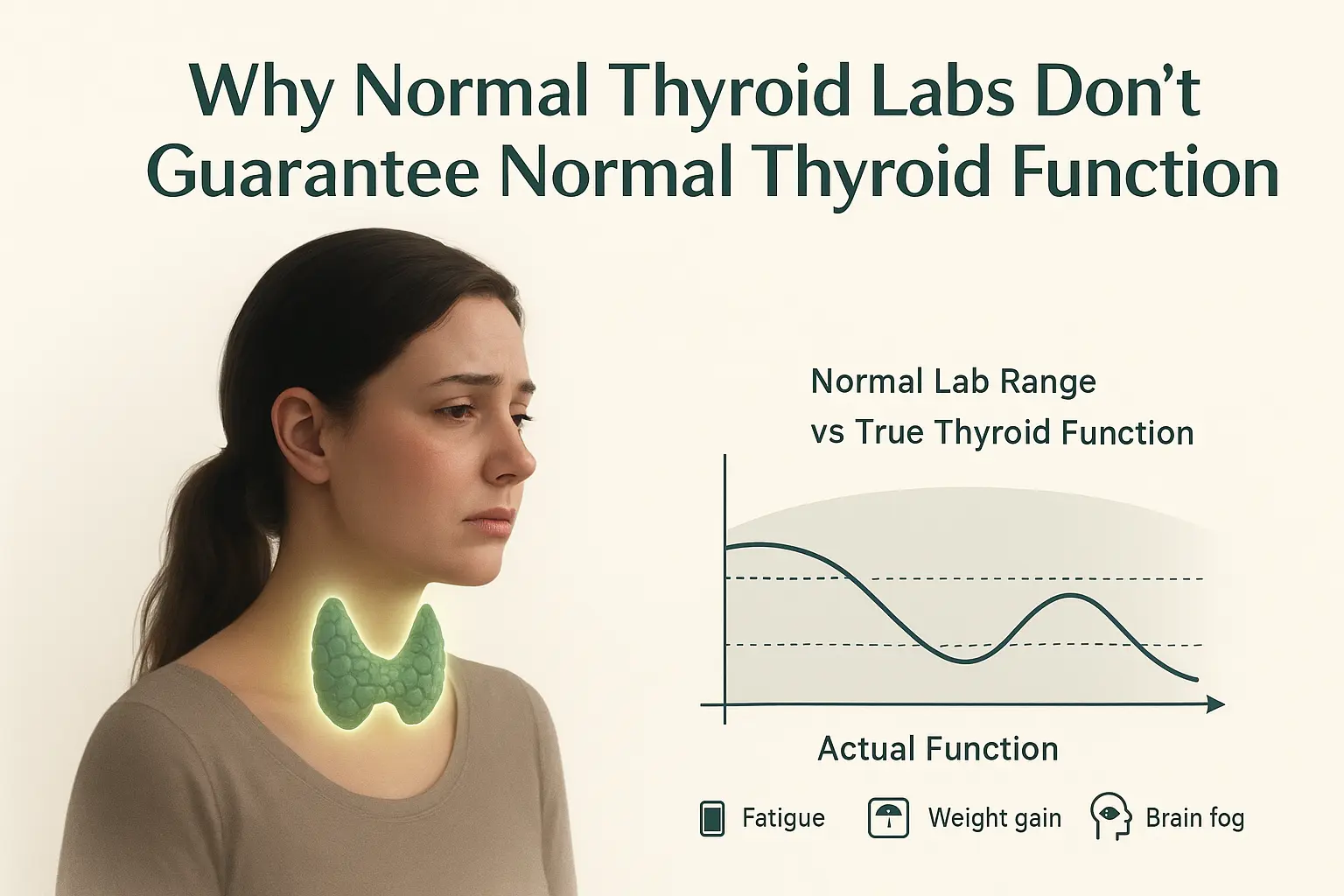
Many women and men feel constantly fatigued, struggle with weight, or notice mood swings — yet routine thyroid labs often appear “normal.” This disconnect can be confusing and frustrating. Understanding how thyroid function interacts with hormones, metabolism, and lifestyle factors is key to recognizing subtle imbalances before they affect energy, mood, and overall well-being.
How Thyroid Hormones Work
The thyroid produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy, and mood. While T4 is the main hormone released, it is inactive and must convert into the active form, T3, to influence your body effectively.
- T4 → T3 conversion is critical for energy production and metabolic efficiency
- T3 affects brain function, metabolism, and fatigue levels- literally everything in the body.
- Conversion can be influenced by stress, diet, lifestyle habits, and many other factors like liver function, etc.
- The availability of T3 can be affected by the amount that is bound up by the binding globulins. Hence, measuring Free T3 is also needed.
Even when labs measure TSH or T4 levels and appear “normal,” subtle dysfunction in T3 conversion or hormone utilization can lead to fatigue and other symptoms.
Why Labs Might Look “Normal”
Routine thyroid tests often focus on TSH or T4 alone, which can miss early or subtle dysfunction. Several factors can influence lab results:
- Timing of the test (morning vs. afternoon)
- Temporary stress or illness
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Minor metabolic disruptions that don’t appear on standard panels
This is why some individuals feel symptoms even when tests suggest everything is fine.
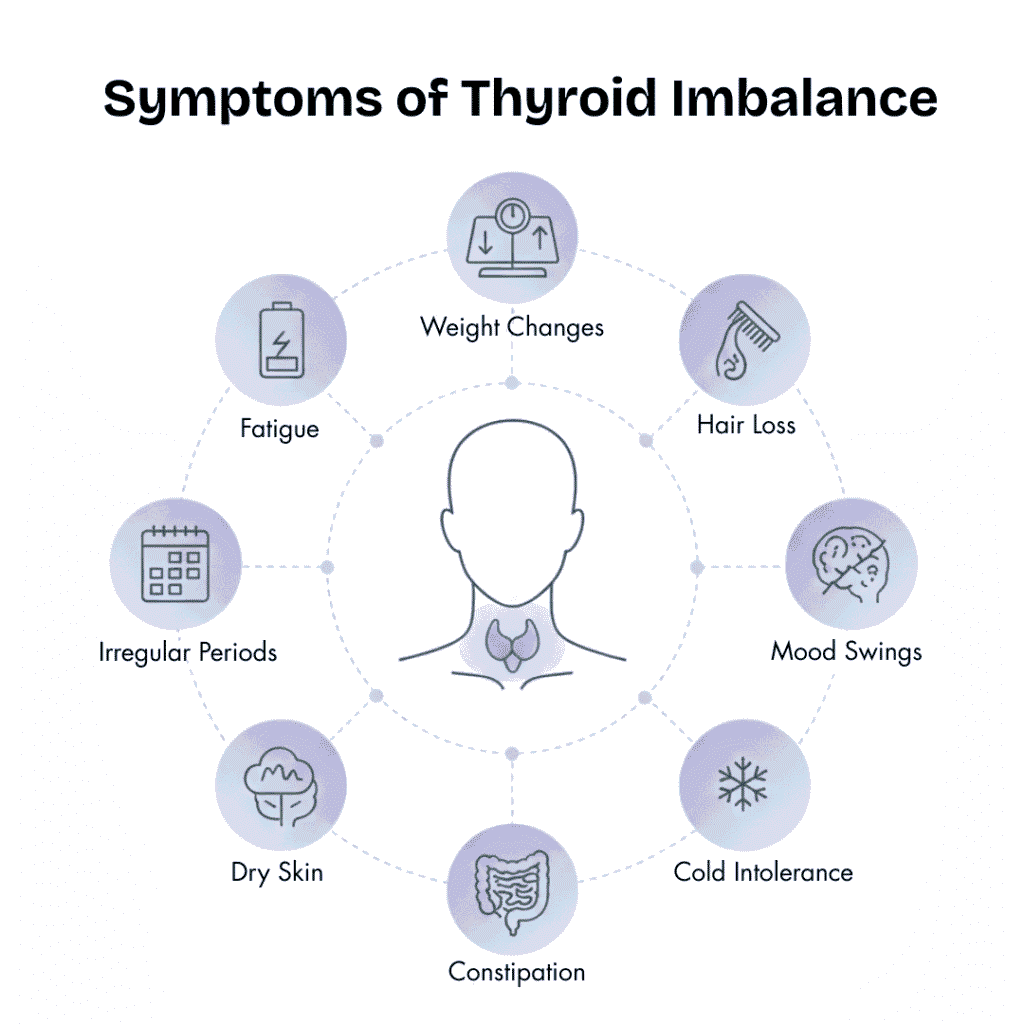
Subtle Symptoms That Often Go Unnoticed
Thyroid imbalance doesn’t always trigger obvious lab alerts. Early signs can include:
- Persistent fatigue, especially after meals
- Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
- Afternoon energy slumps
- Mood swings or irritability
- Minor, unexplained weight fluctuations
Even mild symptoms can indicate that your thyroid is not functioning optimally, despite normal lab values.
Lifestyle & Functional Factors Influencing Thyroid
Functional medicine emphasizes understanding root causes beyond standard labs. Some of the factors that can subtly impact thyroid hormone function are:
- Stress: High cortisol levels can reduce T4 → T3 conversion
- Nutrition: Deficiencies in selenium, iodine, or zinc can affect both conversion and metabolism
- Sleep disruption: Inconsistent sleep can impact hormone balance
- Gut health & inflammation: Chronic issues may influence thyroid function indirectly
Thyroid Hormones – Bound vs Free
- Bound Hormones: Attached to proteins, inactive, measured in standard lab tests.
- Free Hormones: Unbound, active, ready to fuel your cells.
- Why it matters: Only free hormones regulate energy, metabolism, and mood. Even with normal labs, low free hormone levels can leave your body starved for thyroid activity.
Key Nutrients That Support Healthy Thyroid Hormone Production

The thyroid requires certain nutrients and vitamins to function optimally:
- Minerals: Iron, Iodine, Tyrosine, Zinc, Selenium
- Vitamins: E, B2, B3, B6, C, D
- Why it matters: Deficiencies can slow hormone production, leading to fatigue, low energy, and sluggish metabolism.
- Practical Tip: Include leafy greens, eggs, nuts, seeds, and seafood to naturally support thyroid health.
Factors That Can Reduce Thyroid Hormone Production
Certain conditions or exposures can decrease your thyroid’s hormone output:
- Lifestyle & environmental factors: stress, infections, trauma, medications, radiation, fluoride, toxins
- Health conditions: autoimmune diseases
- Signs of reduced hormone production: fatigue, mood swings, unexplained weight changes
T4 → T3 Conversion: How Your Thyroid Makes Hormones Active
- The thyroid releases T4 (inactive), which must be converted into T3 (active) to fuel cells efficiently.
- Supports Conversion: Selenium and Zinc
- Blocks Conversion / Increases Reverse T3: Stress, trauma, low-calorie diets, inflammation, toxins, infections, liver/kidney issues, or certain medications
Improving How Your Cells Respond to Thyroid Hormones
Even if hormone levels are normal, cells must respond properly to them for energy and metabolism:
- Supports Cellular Sensitivity: Vitamin A, Zinc, and regular exercise
- Lifestyle Factors: Prioritize consistent sleep, a balanced diet, and stress management
- Outcome: Ensures thyroid hormones reach your cells effectively, regulating energy, metabolism, and overall well-being
Practical Steps to Support Thyroid Function
Even without abnormal labs, small lifestyle adjustments can support optimal thyroid function:
- Balanced diet: Include protein, fiber, and micronutrients to stabilize blood sugar and hormone function
- Daily movement: Light resistance training or walking improves metabolism
- Sleep hygiene: Prioritize 7–8 hours of consistent sleep
- Stress management: Mindfulness, journaling, or breathing exercises help reduce cortisol
- Monitor symptoms: Track energy patterns, mood, and cravings to notice subtle imbalances
These actions support hormone balance and metabolic health, providing noticeable improvements over time.
Conclusion
Normal thyroid labs don’t always guarantee optimal thyroid function. Subtle disruptions in hormone conversion, lifestyle factors, and stress can affect energy, mood, and metabolism. Understanding these patterns empowers you to notice early signals and take actionable steps toward better hormone health.
At Hormone Reset, we guide individuals to understand metabolic and hormone patterns using functional approaches — emphasizing lifestyle, nutrition, and energy optimization without relying solely on routine lab tests.
References:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9987447/ PMC
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5075641/ PMC
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3356062/ PMC
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30029851/ PubMed
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35015701/ PubMed
FAQs: Understanding Thyroid Function Beyond Lab Tests
1. Can I have thyroid issues even if my blood tests are normal?
Yes. Subtle thyroid imbalances can occur due to T3 conversion issues, lifestyle factors, or stress, which routine labs may not detect. Paying attention to energy, mood, and metabolism is key.
2. What are early signs of thyroid imbalance to watch for?
Common patterns include persistent fatigue, brain fog, mood swings, afternoon energy slumps, and unexplained weight changes, even if lab results appear normal.
3. How can lifestyle influence thyroid function?
Balanced nutrition, regular sleep, stress management, and moderate exercise all support healthy thyroid metabolism and hormone balance. Small adjustments often make a noticeable difference in energy levels.
4. Can stress or sleep affect thyroid labs?
Yes. Stress hormones like cortisol and disrupted sleep can impact T4 → T3 conversion, which may cause symptoms even when standard lab values seem normal.
5. Where can I learn more about supporting hormone balance naturally?
For educational insights on hormone and metabolic patterns, you can explore Hormone Reset, which focuses on functional approaches to energy, metabolism, and hormone balance.