Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterised by a combination of symptoms related to hormonal imbalances and the presence of small cysts on the ovaries.
The cause of PCOS is a combination of unhealthy lifestyle, toxin overload and environmental factors. Insulin resistance, which affects the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, is often associated with PCOS and can contribute to hormone imbalances.

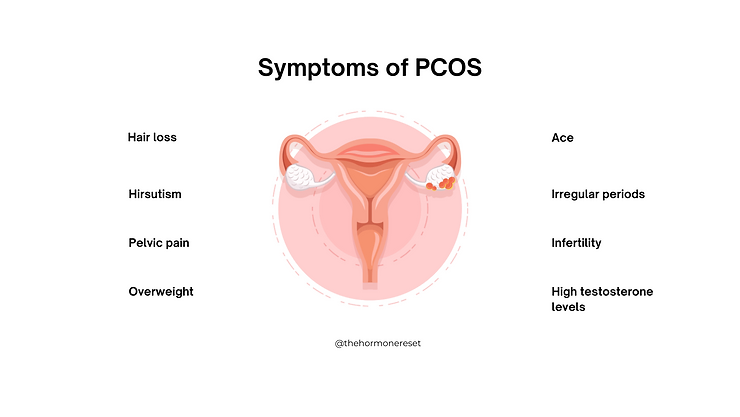
The symptoms of PCOS can vary from person to person, and not all women will experience the same symptoms. Common symptoms of PCOS include:
- Irregular periods: Women with PCOS may have infrequent or prolonged menstrual cycles, or they may experience heavy or unpredictable bleeding.
- Ovarian cysts: The ovaries may contain small cysts, which are fluid-filled sacs. These cysts are usually harmless but can contribute to hormone imbalance if they don’t regress themselves, and rather grow in size.
- Hormonal imbalances: Women with PCOS often have higher levels of androgens, which are male hormones. This can lead to symptoms such as acne,hair thinning, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), and male-pattern baldness.
- Weight gain and difficulty losing weight: Most women with PCOS struggle with weight management. Insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances can make it more challenging to maintain a healthy weight.
- Skin problems: PCOS can be associated with skin issues, including acne, oily skin, and dark patches of skin (acanthosis nigricans).
- Fertility issues: PCOS is one of the leading causes of female infertility. Hormonal imbalances can interfere with the normal ovulation process, making it more difficult to conceive.
It’s important to note that the symptoms of PCOS can vary in severity, and not all women with PCOS will experience all of these symptoms. If you are one who is struggling with PCOS symptoms, certain nutrition interventions can help you manage symptoms and even reverse PCOS.
Here are nine PCOS nutrition interventions that you should incorporate in your daily regime:
- 1. Low-Glycemic Index (GI) Diet: Opt for a balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and low-GI carbohydrates. Low-GI foods help stabilise blood sugar levels and can aid in weight management, a common concern for women with PCOS.
- 2. Fiber-Rich Foods: Include fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet. High-fiber foods can help regulate blood sugar levels, improve digestion, and promote satiety, which may aid in weight management.
- 3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Incorporate omega-3 fatty acids into your diet through sources like fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts. Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce insulin resistance and improve lipid profile in women with PCOS.
- 4. Use Anti-Inflammatory herbs in diet: Consume foods with anti-inflammatory properties, including turmeric, ginger, cinnamon, clove etc. Also have a diet combination of green leafy vegetables, berries, and nuts. Chronic inflammation is often associated with PCOS, and an anti-inflammatory diet will help reduce inflammation and related symptoms.
- 5. Include chromium & sulphur rich foods: Consider adding chromium & sulphur -rich foods such as broccoli, green beans, nuts, and whole grains to your diet. Chromium supplementation improves insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism in women with PCOS.
- 6. Get sufficient Vitamin D: Ensure adequate vitamin D levels through sunlight exposure and/or vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, and egg yolks. Vitamin D deficiency is prevalent in women with PCOS and may contribute to insulin resistance.
- 7. Probiotics to be added daily: Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, or consider probiotic supplements. Probiotics help improve gut health, reduce inflammation, and regulate hormonal balance in women with PCOS.
- 8. Herbal Remedies: Certain herbal remedies like cinnamon, spearmint tea, and saw palmetto have beneficial effects on insulin sensitivity and hormone levels in women with PCOS. However, consult with a healthcare provider before using herbal supplements.
- 9. Mindful Eating: Practise mindful eating techniques, such as paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and savouring each bite. Mindful eating can promote a healthy relationship with food and support weight management goals in women with PCOS.
References :
- Marsh K, et al. (2010). The effect of a low glycemic load diet on acne vulgaris and the fatty acid composition of skin surface triglycerides. J Dermatol Sci. 59(3):248-251.
- Palomba S, et al. (2015). Dietary Interventions and Nutritional Supplements for Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. PCOS Consensus Workshop Group. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 16(3):269-284.
- Mohammadi E, et al. (2012). Effects of omega-3 fatty acids supplementation on serum adiponectin levels and some metabolic risk factors in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 21(4):511-518.
- Wang J, et al. (2016). Effects of probiotics on glycaemic control, lipid profiles, and endothelial function in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Endocrine. 52(1):69-77.
Share



Leave a Reply