Table of Contents:
An Introduction
Mental health is a cornerstone of overall well-being, yet millions of people worldwide grapple with challenges like anxiety, depression, chronic stress, and mood disorders. While traditional mental health care often emphasizes symptom management, a growing number of practitioners and patients are turning to functional medicine for mental health—a holistic, root-cause-driven approach that seeks to transform lives by addressing underlying imbalances. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what functional medicine is, how it supports mental health, and why it deserves a leading role in your wellness journey.
How Functional Medicine Supports Mental Health
Functional medicine for mental health focuses on identifying and addressing the root causes of emotional and cognitive challenges. Rather than simply prescribing medication to manage symptoms, functional medicine practitioners use advanced diagnostics and personalized interventions to uncover triggers that may be overlooked in conventional care. These can include chronic inflammation, hormonal imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, gut health disturbances, chronic stress, and even environmental toxins.
This patient-centered philosophy helps uncover and resolve hidden contributors to mental health symptoms, often leading to more sustainable improvements in mood, cognition, and overall vitality.
What is Functional Medicine?
Functional medicine is an advanced, systems-oriented approach that addresses the underlying causes of disease rather than just treating symptoms. It views the body as an interconnected system, understanding that mental health cannot be separated from physical health. Practitioners of functional medicine use cutting-edge diagnostics, detailed health histories, and lifestyle interventions—such as nutrition, exercise, sleep optimization, and stress reduction—to restore optimal function and balance.
For example, a person experiencing depression might have underlying gut dysbiosis, chronic inflammation, or thyroid dysfunction all of which can impact brain chemistry and mood. By identifying these factors, functional medicine practitioners can design targeted interventions that support mental well-being at its core.

Benefits of Functional Medicine for Mental Health
- Personalization: Each individual receives a tailored plan based on unique genetics, lifestyle, and health history. No two treatment protocols are exactly the same.
- Root Cause Resolution: Instead of masking symptoms, functional medicine addresses the underlying drivers of mental health issues, aiming for lasting change
- Integrative Therapies: Approaches may include nutritional therapy, targeted supplementation, stress management, sleep optimization, and detoxification—often leading to more sustainable results.
- Empowerment: Patients become active participants in their healing journey, equipped with education and practical tools to support lifelong mental wellness.
Common Root Causes Addressed in Functional Medicine for Mental Health
- Gut-Brain Connection: Research shows that gut health profoundly impacts mood and cognition. Imbalances in the gut microbiome can contribute to anxiety, depression, and brain fog.
- Chronic Inflammation: Inflammation in the body and brain is linked to various mental health disorders. Functional medicine seeks to identify and reduce sources of inflammation.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Thyroid, adrenal, and sex hormone imbalances can cause mood swings, irritability, fatigue, and depression.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins (such as B12, D, folate), minerals (magnesium, zinc), and essential fatty acids can negatively affect neurotransmitter function and mood regulation.
- Environmental Toxins: Exposure to heavy metals, mold, and other toxins can disrupt brain chemistry and contribute to psychiatric symptoms.
- Chronic Stress & Trauma: Ongoing stress or unresolved trauma can alter brain structure and function, increasing vulnerability to mental health issues.
Key Functional Medicine Strategies for Mental Health
- Comprehensive Lab Testing: Functional medicine practitioners use advanced testing to identify hormonal, nutritional, or metabolic imbalances that may be affecting mental health.
- Personalized Nutrition Plans: Diets rich in brain-supportive nutrients—such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and B vitamins—are tailored to each individual’s needs.
- Gut Health Restoration: Strategies may include probiotics, prebiotics, and anti-inflammatory diets to support a healthy gut microbiome.
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Mindfulness, yoga, meditation, and biofeedback are used to calm the nervous system and build resilience.
- Detoxification Protocols: These are designed to reduce the body’s burden of environmental toxins, supporting clearer thinking and emotional balance.
- Targeted Supplementation: Supplements are recommended based on lab results and individual needs—common examples include vitamin D, magnesium, and adaptogenic herbs.
The Link Between Hormones, Functional Medicine, and Mental Health
Hormonal balance is central to both physical and mental health. Imbalances in thyroid hormones, cortisol (the stress hormone), estrogen, and testosterone can have profound effects on mood, cognition, and emotional stability. For instance, low thyroid function may present as depression, while chronic high cortisol can lead to anxiety and sleep disturbances. Functional medicine practitioners are uniquely equipped to assess and correct these imbalances using natural, evidence-based interventions, leading to lasting improvements in mental health
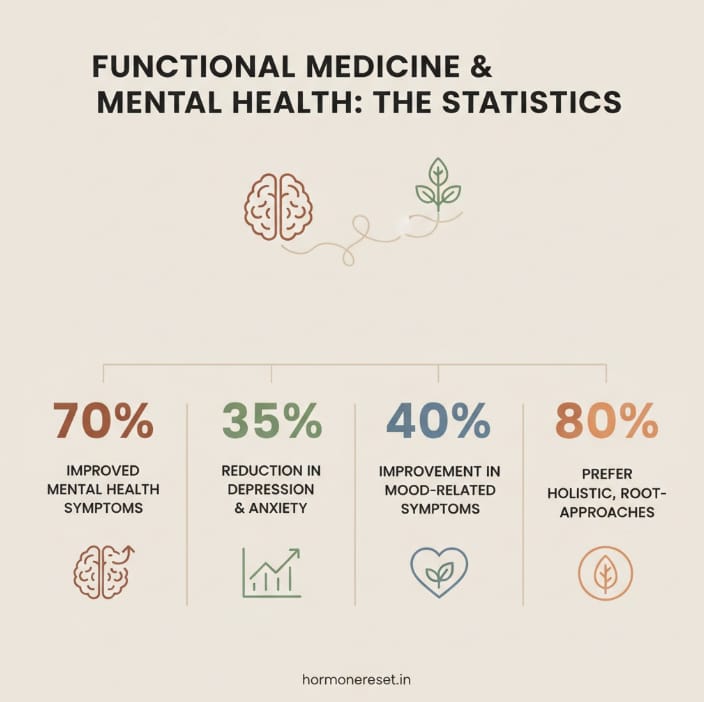
Real-Life Example: Functional Medicine in Action
Consider a case where a patient with persistent anxiety and fatigue underwent functional medicine evaluation. Comprehensive lab tests revealed low vitamin D, mild hypothyroidism, and gut dysbiosis. Through a combination of dietary changes, vitamin D supplementation, gut-healing protocols, and stress management, the patient experienced significant improvements in mood, energy, and resilience—without relying solely on psychiatric medication.
Success Stories and Scientific Backing
Research is increasingly validating the functional medicine approach. Studies show that interventions targeting gut health, inflammation, and nutrition can significantly improve symptoms of depression, anxiety, and even severe mental health conditions. For example, a 2022 study published in Frontiers in Psychiatry found that personalized nutrition and gut-focused therapies led to measurable improvements in mood and cognitive function. Many individuals report life-changing transformations—finding relief where conventional approaches fell short.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is functional medicine for mental health?
Functional medicine for mental health is a holistic approach that addresses underlying causes—like inflammation, nutrient deficiencies, and hormonal imbalances rather than just managing symptoms.
How does functional medicine differ from traditional mental health care?
Traditional care often focuses on medication and symptom management. Functional medicine for mental health emphasizes personalized, root-cause solutions and lifestyle interventions
Can functional medicine help with anxiety and depression?
Yes. By addressing root causes such as gut health, nutrition, and hormones, functional medicine can support improvements in anxiety, depression, and overall mental well-being.
Is functional medicine safe to use alongside my current treatment?
Functional medicine is typically complementary to conventional care. Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes to your mental health regimen.
How long does it take to see results?
Results vary, but many people notice improvements within a few weeks to a few months as underlying imbalances are addressed.
Is Functional Medicine Right for You?
If you’re seeking a more holistic, proactive approach to mental health, functional medicine offers a promising path. By addressing the interconnected systems of the body and mind, it opens the door to deeper healing and resilience. Whether you’re struggling with ongoing mood issues or simply want to optimize your emotional well-being, functional medicine can provide answers and lasting relief.
Conclusion
Functional medicine is ushering in a new era for mental health care—one that values personalization, root-cause resolution, and patient empowerment. If you or a loved one are struggling with mental health challenges, consider exploring functional medicine as a powerful ally on your journey to lasting well-being.
Ready to explore functional medicine for your mental health?
Book a Free Discovery call at hormonereset.in for a personalized consultation.